Stem Cell Therapy
The Future of Regenerative Medicine
WHAT STEM CELLS DO
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Adipose-derived stem cells have a wide range of applications in treating diseases caused by the dysfunction of organs and tissues. These cells have been used to address conditions such as cirrhosis, diabetes, hypertension, Parkinson’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, adipose-derived stem cells play a significant role in anti-aging treatments, promoting tissue regeneration and cellular repair to help slow down the effects of aging.
Urine-Derived Stem Cells
Urine-derived stem cells (UDSCs) have shown exceptional promise in the treatment of kidney and genitourinary diseases. Groundbreaking research has led to the discovery of their ability to secrete klotho, a protein linked to kidney function and aging. The world’s first phase 1 clinical trial using autologous UDSCs for chronic kidney disease (CKD) has opened new possibilities in regenerative medicine.
Immune Cells
Immune cells, including Natural Killer (NK) cells, T cells, and Dendritic Cells (DCs), play a vital role in eliminating foreign substances and fighting diseases, including cancer. These specialized cells detect and destroy harmful pathogens, remove toxins, and regulate immune system responses, helping the body maintain a healthy balance and prevent autoimmune diseases.
Development of Cell Therapeutics
Stem cell research has led to significant advancements in therapeutic treatments. The world’s first phase 2 clinical trial involving adipose-derived stem cell intravenous injections for atopic dermatitis marks a major milestone in regenerative medicine. Additionally, stem cell-based therapies have been extensively explored for autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, offering new hope for long-term treatment solutions.
Stem Cell Conditioned Media
Stem cell-conditioned media contain essential growth factors and cytokines such as EGF, FGF, VEGF, fibronectin, and collagen, which contribute to skin repair and anti-aging. These formulations are widely used in skincare and medical aesthetics, with SupremeX™ providing optimal stem cell culture environments for research and therapeutic applications in over 50 countries worldwide.
WHAT IS STEM CELL?
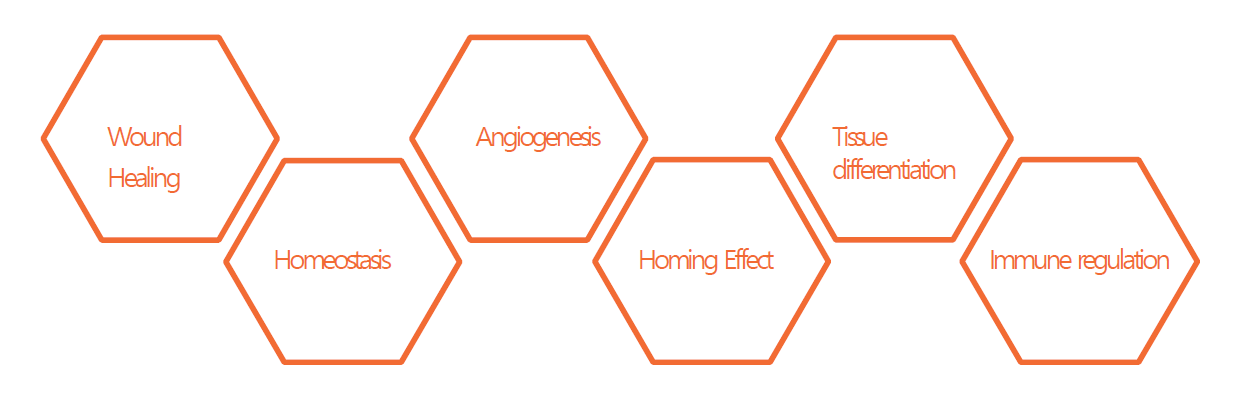
Characteristics of Stem Cells
- Self-Renewal: Stem cells can replicate and produce identical cells with regenerative properties.
- Multipotential Differentiation: These cells can develop into various tissues and organs, such as the heart, bones, nerves, skin, and liver.
- Homing Effect: When introduced into the body, stem cells naturally migrate to damaged areas, promoting healing and regeneration.
Functions of Stem Cells
- Wound Healing: Stem cells regenerate damaged tissues and promote recovery.
- Cell Differentiation: These cells transform into specialized cells required by the body.
- Growth Factor Activation: Stimulate the production of essential hormones, collagen, and other regenerative elements.
- Immune Regulation: Enhance immune system function and protect against infections.
- Cell Death Prevention: Prevent premature cell degeneration and aging.
- Angiogenesis: Promote the formation of new blood vessels, ensuring better circulation and tissue repair.
Types of Stem Cells
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Highly versatile cells that can differentiate into any tissue type.
- Adult Stem Cells: Found in bone marrow, fat, and umbilical cord blood, these cells can regenerate specific tissues.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): Genetically reprogrammed somatic cells that mimic embryonic stem cells’ regenerative abilities.
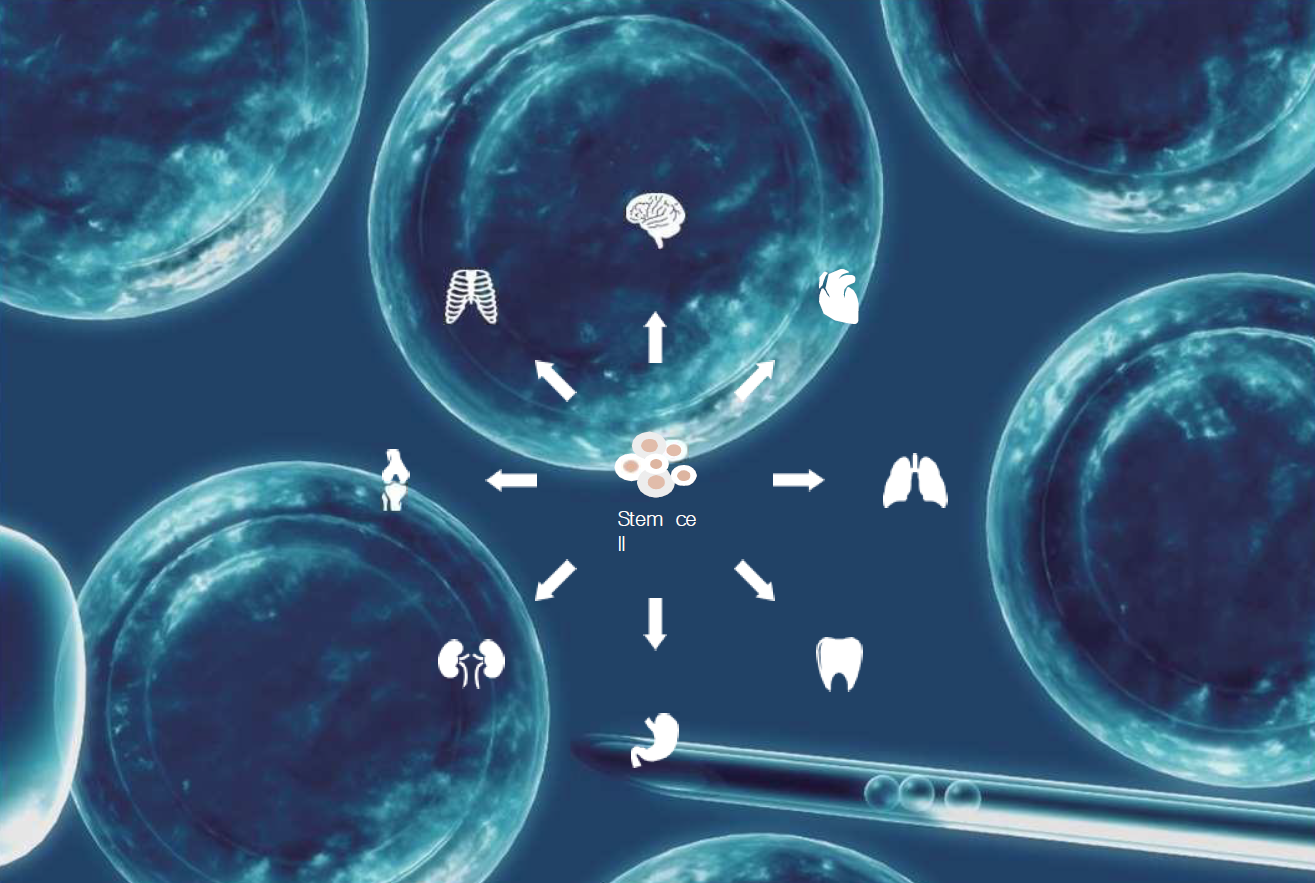
AUTOLOGOUS STEM CELLS
Customized Stem Cell Therapy for Targeted Healing
Autologous stem cell treatments offer highly personalized solutions by tailoring stem cell applications to an individual’s medical condition. Through a one-on-one approach, these therapies provide optimal healing outcomes, helping patients recover from degenerative diseases, injuries, and aging-related conditions.
Dual Administration for Maximum Effectiveness
Stem cells can be introduced into the body through intravenous injections or direct administration to the targeted area. Intravenous delivery ensures widespread circulation, allowing stem cells to locate and repair damaged tissues naturally. Direct injections are used for specific areas such as cartilage, where blood supply is limited. Combining both methods enhances therapeutic outcomes and accelerates the healing process.
TREATMENT CASES
Stem Cell Banking Program – Investing in Future Health
A long-term cryopreservation program allows individuals to store their stem cells for future medical needs. By preserving stem cells from adipose tissue, individuals can access regenerative treatments for unexpected health challenges such as aging-related diseases, injuries, and degenerative conditions. Stem cell banking is a proactive step towards maintaining long-term health and well-being.
Minimally Invasive Stem Cell Processing
The process of harvesting, isolating, and cultivating stem cells is simple and minimally invasive. A one-time liposuction procedure is performed to extract adipose tissue, after which stem cells are processed and stored for future use. Patients can return to their daily activities shortly after the procedure, with minimal downtime required.
IMMUNE CELLS PROTECT YOUR BODY
The Role of the Immune System in Disease Prevention
The immune system acts as the body’s natural defense mechanism, fighting off harmful pathogens, viruses, bacteria, and even cancerous cells. An underactive immune system can lead to chronic infections and diseases, while an overactive immune system can result in allergies or autoimmune conditions.
Types of Immune Cells and Their Functions
- Innate Immunity: Macrophages and Natural Killer (NK) cells provide the first line of defense against infections.
- Acquired Immunity: T cells and B cells recognize and eliminate specific threats, ensuring long-term immunity.
- Dendritic Cells & Gamma Delta T Cells: These cells bridge innate and acquired immune responses, optimizing immune defense mechanisms.
Immune Cells and Cancer Treatment
Cancer occurs when the body’s normal cells mutate and multiply uncontrollably. A healthy immune system can eliminate up to 10 million tumor cells daily. However, when the number of mutated cells exceeds a billion, cancer becomes clinically detectable. Enhancing immune cell function through regenerative therapy can improve the body’s ability to fight cancer and prevent disease progression.
Stem cell and immune cell therapies are transforming the landscape of modern medicine, providing innovative solutions for disease treatment, tissue regeneration, and overall wellness. Through advanced research and clinical applications, these therapies are paving the way for a healthier, longer life.