- 836 Nonhyeon-ro, Sinsa-dong, Gangnam, Seoul, South korea
Rhinoplasty
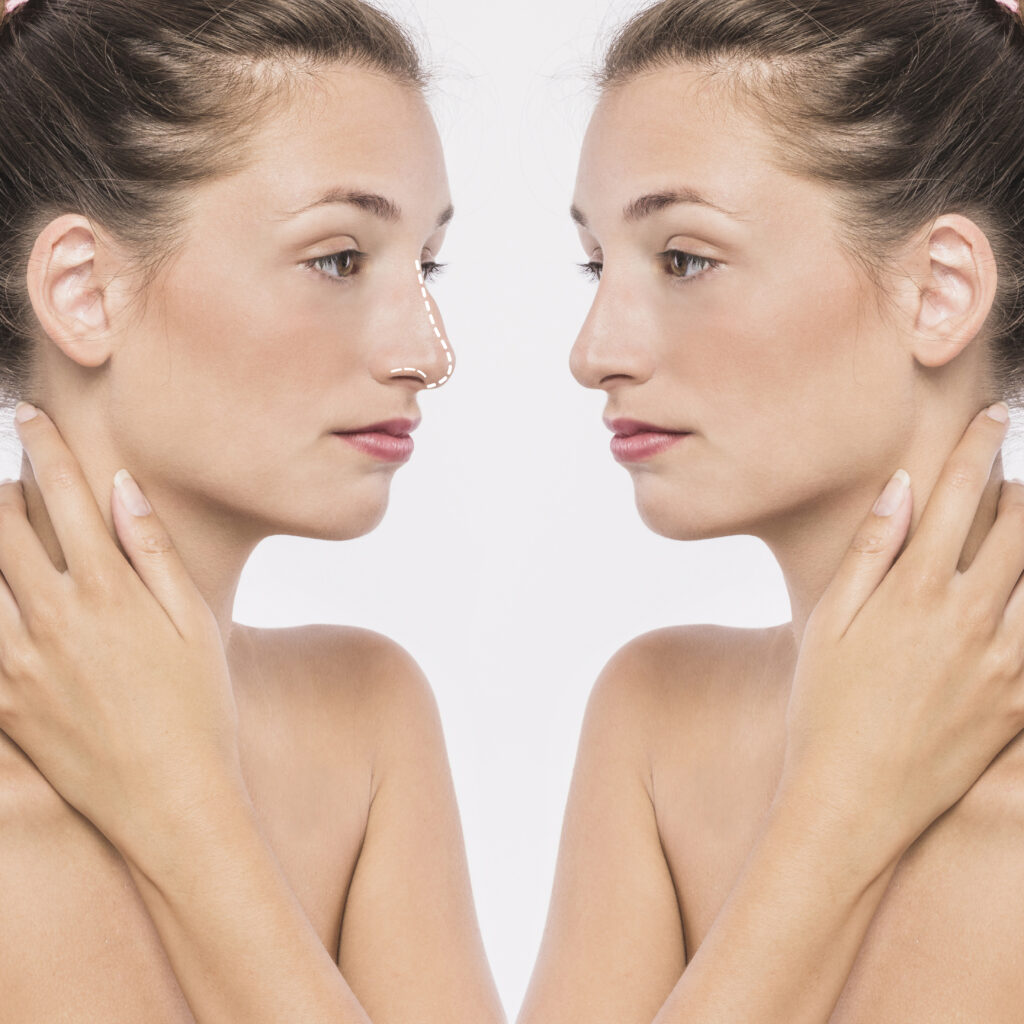

Rhinoplasty in South Korea – A Complete Guide
South Korea is renowned for its cutting-edge rhinoplasty procedures, world-class plastic surgeons, and state-of-the-art medical facilities. Whether you’re looking for a subtle enhancement or a complete transformation, South Korea offers advanced techniques to achieve natural and harmonious results.
In this guide, we will cover the different types of rhinoplasty procedures, why South Korea is a top choice for nose surgery, and how to prepare for your procedure. We’ll also discuss what to expect before, during, and after rhinoplasty, along with aftercare tips to ensure optimal healing.
What Is Rhinoplasty?
Rhinoplasty, commonly referred to as a “nose job,” is a cosmetic or reconstructive procedure that reshapes the nose for aesthetic or functional improvements. South Korea has become a global leader in rhinoplasty due to its innovative surgical techniques, advanced technology, and skilled plastic surgeons.
Whether you need correction for a nasal hump, wide nostrils, a deviated nose, or tip refinement, South Korean clinics offer customized solutions for every patient.
Why Choose South Korea for Rhinoplasty?
South Korea is considered the “Plastic Surgery Capital of the World”, with over a million cosmetic procedures performed annually. Here’s why patients from around the globe choose South Korea for rhinoplasty:
-
Highly Skilled Surgeons – Board-certified plastic surgeons with years of specialized training.
-
Advanced Techniques – 3D imaging, minimally invasive procedures, and personalized surgery plans.
-
Natural Results – Emphasis on achieving balanced, symmetrical, and natural-looking noses.
-
State-of-the-Art Clinics – Equipped with the latest medical technology and safety standards.
-
Affordable & High-Quality – Competitive pricing compared to Western countries without compromising quality.
-
Comprehensive Medical Tourism Services – Includes consultations, airport pick-up, accommodations, and aftercare.
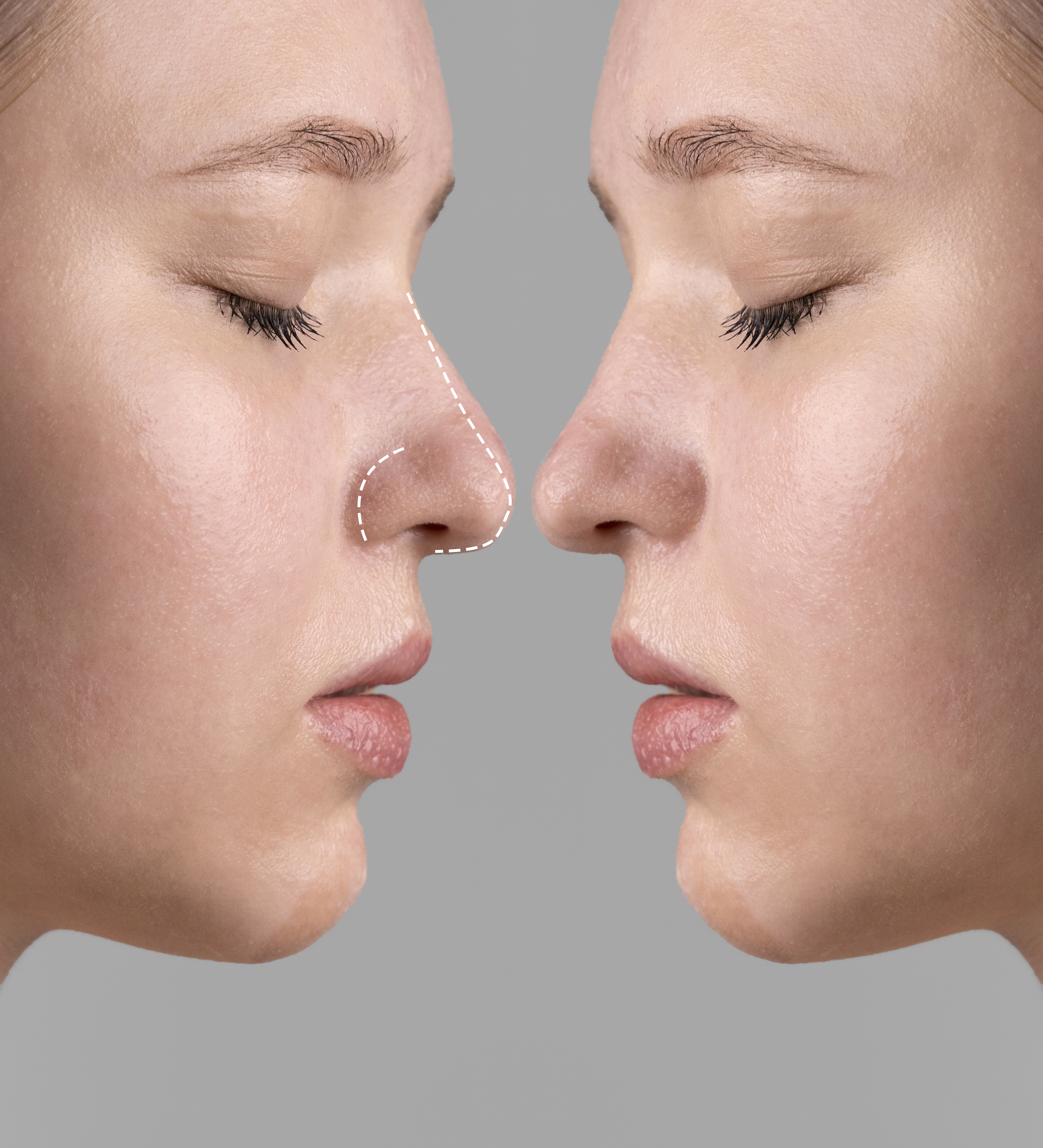
Types of Rhinoplasty in South Korea
South Korean plastic surgeons specialize in various types of rhinoplasty procedures based on individual facial structures and aesthetic goals.
1. Standard Rhinoplasty
This procedure reshapes the nose bridge, tip, and structural support using high-quality implants or cartilage grafts.
-
Nose Bridge Enhancement – Silicone, Goretex, or autologous cartilage implants for height adjustment.
-
Tip Refinement – Reshaped using septal or ear cartilage for a softer, natural look.
-
Structural Support – Reinforcement using nasal, ear, or rib cartilage.
2. Long or Downward Pointing Nose
A drooping nasal tip can create an aged appearance. Two common correction methods include:
-
Cartilage Repositioning – Adjusting the nasal cartilage to lift and balance the tip.
-
Cartilage Repositioning & Bridge Implant – A combination of repositioning and bridge enhancement for additional support.
3. Short Upturned Nose
An upturned nose exposes excessive nostrils. Correction techniques include:
-
Cartilage Extension – Lengthening the nose with septal or rib cartilage.
-
Augmentation Rhinoplasty – Enhancing the nose structure using implants or grafts.
4. Deviated Nose
A crooked nose can be congenital or due to injury. The correction method is:
-
Septoplasty – Realignment of the nasal septum for improved symmetry and breathing.
5. Hump Nose (Aquiline Nose)
A prominent dorsal hump can be corrected through:
-
Nose Rasping – Minor hump reduction by shaving the nasal bone.
-
Fracturing & Reshaping – If the hump is larger, controlled fractures are performed.
6. Wide Nose (Osteotomy)
A broad nose can be slimmed using:
-
Osteotomy – Precision bone cuts to narrow the nose structure.
7. Nose Tip Surgery
Tip rhinoplasty is ideal for those with a bulbous or undefined nose tip. It involves:
-
Cartilage Reshaping – Refining the nasal tip for better definition.
-
Tip Plasty – Precise sculpting for a more pointed, elegant tip.
8. Alar Reduction
Wide nostrils can be narrowed using:
-
Nostril Base Reduction – Removing excess skin and suturing for a refined look.
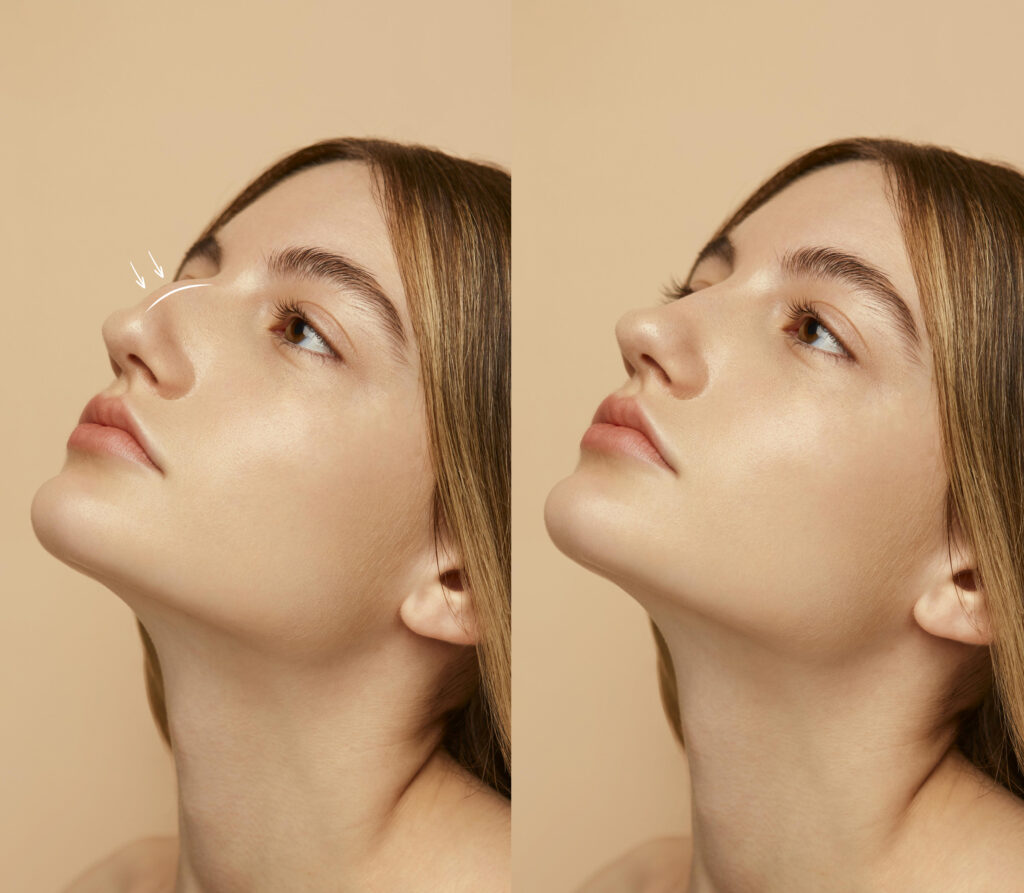

Limitations of Rhinoplasty
While rhinoplasty can significantly enhance facial harmony, it’s essential to consider the limitations:
-
Age Restrictions – Recommended for individuals over 18 unless medically necessary.
-
Healing Time – Full results take up to a year.
-
Structural Limitations – Overcorrection can impact nasal function.
-
Risk of Complications – Includes swelling, infection, or breathing issues.
Book Now
Make An Appointment
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eius tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim adiqua minim veniam quis nostrud exercitation ullamco incididunt magna aliqua veniam quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip
Opening Hours
Monday - Thursday
- 08.00 AM - 20.00 PM
Friday
- 08.00 AM - 17.00 PM
Saturday
- 09.00 AM - 14.00 PM
Sunday
- 09.00 AM - 18.00 PM

